
Climate change can feel complex and controversial. We are here to help you, so we have created a glossary for you to become a sustainability genius and be part of the movement!
Carbon footprint
The amount of carbon emitted by an individual or organization in a given period of time.
Greenhouse gasses
GHG is the short term for greenhouse gasses. They absorb rays from the sun and redistribute them as radiation in the earth's atmosphere. That process is called the greenhouse effect. There are 40 greenhouse gasses but the most common ones are 7; (CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorinated hydrocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride.) CO2 emissions make up to 76% of the GHGs.
Carbon Accounting
In its simplest form - carbon accounting is the process that organizations use to measure their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions so they can fully understand their carbon footprint and set targets to reduce their emissions.
What is the difference between CO2 and CO2e?
CO2 accounts for carbon dioxide - the most common GHG emitted by human activities.
CO2e is a term for describing different greenhouse gasses in a common unit. It accounts for carbon dioxide and all the other gasses as well; methane, nitrous oxide etc.

Carbon neutral, climate positive, carbon negative, climate neutral, net zero carbon emissions, net zero emissions? We know it can be confusing..
Carbon neutral means that the CO2 released into the atmosphere is balanced by an equivalent amount of being removed.
Climate positive means that activity goes beyond achieving net-zero carbon emissions to create an environmental benefit by removing additional carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Carbon negative means the same as “Climate positives”
Carbon positive is how organizations describe climate positive and carbon negative. It is mainly a marketing term and understandably confusing.
Climate neutral refers to reducing all greenhouse gasses to the point of zero while eliminating all other negative environmental impacts an organization may cause.
Net zero emissions balance the amount of greenhouse gasses released and the amount removed from the atmosphere.

1.5 degrees - what's the deal?
According to the Paris Agreement, the 1.5C trajectory refers to the path we should take to get to net zero by 2050 compared to pre industrial levels.
Sustainability
“sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” UN World
What are Sustainable Development Goals?
The blueprint to achieve better and a more sustainable future for all. It consists of 17 Goals which are all interconnected, and in order to leave no one behind - we must achieve them before 2030.

The Greenhouse Gas Protocol
The most recognized standard for measuring and managing emissions.
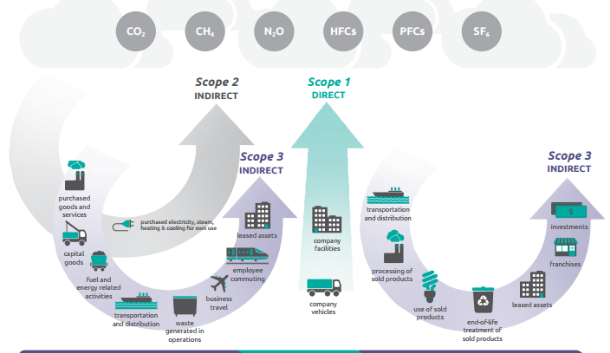
Scope 1,2 & 3
A company’s greenhouse gas emissions are classified into three scopes. Scope 1 and 2 are mandatory to report, whereas scope 3 is voluntary and the hardest to monitor. However, companies succeeding in reporting all three scopes will gain a sustainable competitive advantage.
Scope 1 emissions:
Known as direct emissions, these are emissions from activities owned or controlled by an organization. Examples include emissions from combustion in owned or controlled boilers, furnaces and vehicles; and emissions from chemical production in owned or controlled process equipment.
Scope 2 emissions:
Called indirect emissions, these are associated with an organization’s consumption of electricity, heat, steam and cooling. They are a consequence of an organization’s activities or choice of supplier, but occur at sources the business does not directly own or control. Examples would be air-conditioning and electricity use for lighting, lifts and IT equipment.
Scope 3 emissions:
These are the wider-reaching emissions caused by the value chain of business operation. Examples are business travel or the transport of goods to or from a site. Or the sourcing of raw materials, development of product packaging and the disposal of waste. Scope 3 emissions also include the lifetime emissions of sold products. Car manufacturers, for example, must account for the emissions of each car when it is in use.
What is greenwashing?
Greenwashing is a form of misleading marketing or communication, where a product, service or company is presented as “better” in respect to climate change, the environment or animal and human rights issues, without proper documentation to back this claim.
What does the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) do?
Since 1988 the IPCC has been drawing upon scientists to advance knowledge to policymakers and the public on climate change. It is the UN body of assessing the science related to human-caused climate change. The main activity of the IPCC is the preparation of reports assessing the state of knowledge of climate change. Find the latest report here
What is the Kyoto Protocol?
Kyoto Protocol is the protocol attached to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, which sets legally binding commitments on greenhouse gas emissions.
To conclude.
By now you can feel a little more confident about the basic climate change terms.
Feel free to reach out to us and let's help you on your journey towards net zero emissions.
Contact: christel@energi.ai
